The impact of “Greenhouse Effect”
Short wave solar radiation from the sun passes through the conservatory roof & is absorbed by walls & furnishings, converting it into very long wave radiation, which then rises vertically but cannot escape – causing a build up of heat in your conservatory.
During spring & summer, conservatories heat up rapidly to become intensely uncomfortable. Only roof blinds can effectively block rays from the high the sun, & reduce the temperature to comfortable levels. Side blinds have a relatively minor influence, perhaps causing less than 10% of the problem. Many customers find that they do not need side blinds at all, once roof blinds have been fitted, certainly not for thermal reasons. If you are unsure whether you want, or need, side blinds, delay the purchase of them until you have had roof blinds installed & lived through the summer months.
In practice, conservatory heat gain through solar radiation is dependent on numerous factors:
- Position & height of the sun (high sun is the worst)
- Aspect of conservatory (South facing is the most severe)
- Protection from outside buildings & trees
- Pitch & height of conservatory roof
- Glazing thickness & type
- Atmospheric conditions
- Fabric used (aluminium backed is the best)
The principle of the human “comfort zone” helps us understand how air temperature, humidity, mean radiant temperature (MRT*), wind and sunshine affect human comfort.
*MRT is defined as the average temperature experienced from the combination of all the surface temperatures in a conservatory, i.e. from walls, windows, flooring, roof panels, furniture, furnishings, plants & people.
As winter approaches, rabbits shed old skin & fur and grow a new heavier pelt, birds migrate south, and hedgehogs hibernate. When trying to maintain a normal body temperature close to 98.6°F, humans have few natural controls with which to adapt to these changes in climate.
There are three mechanisms to maintain this narrow temperature range:
- the first is heat generated inside the body - by shivering the increased muscle activity and a higher metabolic rate increases internal heat production
- the second is by gaining heat from surroundings; by developing Goose Bumps - body hair is fluffed up to provide better insulation to prevent heat loss.
- the third is by losing heat to the surroundings – by sweating , moisture moves to the skin surface to be evaporated to lower body temperature.
The body automatically makes constant changes to control these mechanisms and regulate body temperature.
- In addition, blood flow is reduced to the hands, feet and skin surface in the winter to reduce heat loss to surroundings, and increased in to these areas in the summer to encourage heat loss.
Air temperature is the most significant factor which affects our internal temperature and our level of comfort. Good quality, truly thermal roof blinds, make a huge difference to the air temperature inside the conservatory, by providing shade & reflecting solar radiation back through the roof during summer; & by reducing heat loss in winter through double glazing by up to 50%.
Marathon runners have a silver sheet wrapped around them at the end of the race, because the body loses heat fast & the foil will reflect the heat back to reduce heat loss, preventing the onset of hypothermia. The use of aluminium in space probes is well documented as it gives maximum thermal protection. The most effective blinds use aluminium on the back of the fabric for the ultimate in thermal performance.
Realistically, when using aluminium backed roof blinds in a south facing conservatory, high summer temperatures can be reduced from 39 degrees C to 27 degrees C. This will of course vary depending on time of year, glazing type, atmospheric conditions & other factors, but transforms your conservatory into a comfortable environment.
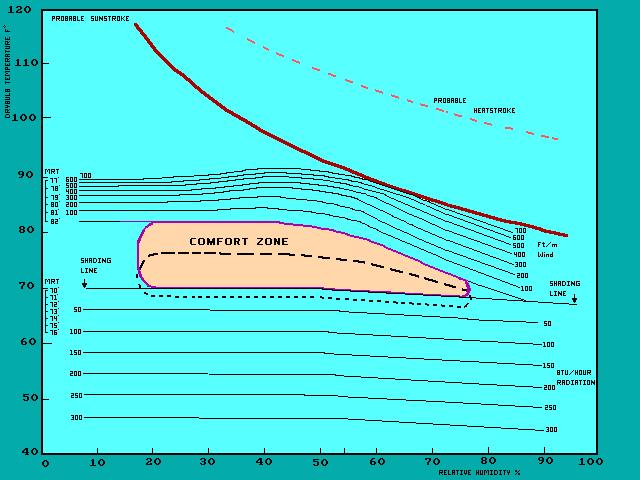
The air temperature is plotted on the vertical axis and relative humidity on the horizontal axis. The shaded area near the centre of the graph shows the combination of temperature and humidity which most people would find comfortable during the summer if they are sitting in the conservatory. The dotted area shows the comfort zone for the winter: It is interesting to see that the human body can actually adjust somewhat to different seasons.
The climatic elements around the comfort zone are shown by means of curves which indicate the nature of corrective measures necessary to restore the feeling of comfort at any point outside the comfort zone. For example the roof blinds would need to be drawn when the temperature is above the comfort zone to provide the necessary shading. When the temperature is below the comfort zone the heating may need to go on, or be turned up, or the roof blinds drawn to keep the heat in.
For the choices available for reducing solar heat, click here.
For comparative analysis of Roof Pleated & Roof Roller, click here
